


This Jmol Exploration was created using the Jmol Exploration Webpage Creator from the MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling.
David S. Goodsell is a molecular biologist and artist who writes the Protein Data Bank Molecule of the Month feature, which explores the structure and function of a different protein each month. Dr. Goodsell's molecular landscapes depict proteins in context, displaying their size, structure, concentration, location and interacting partners in an aesthetically pleasing but information-rich context.
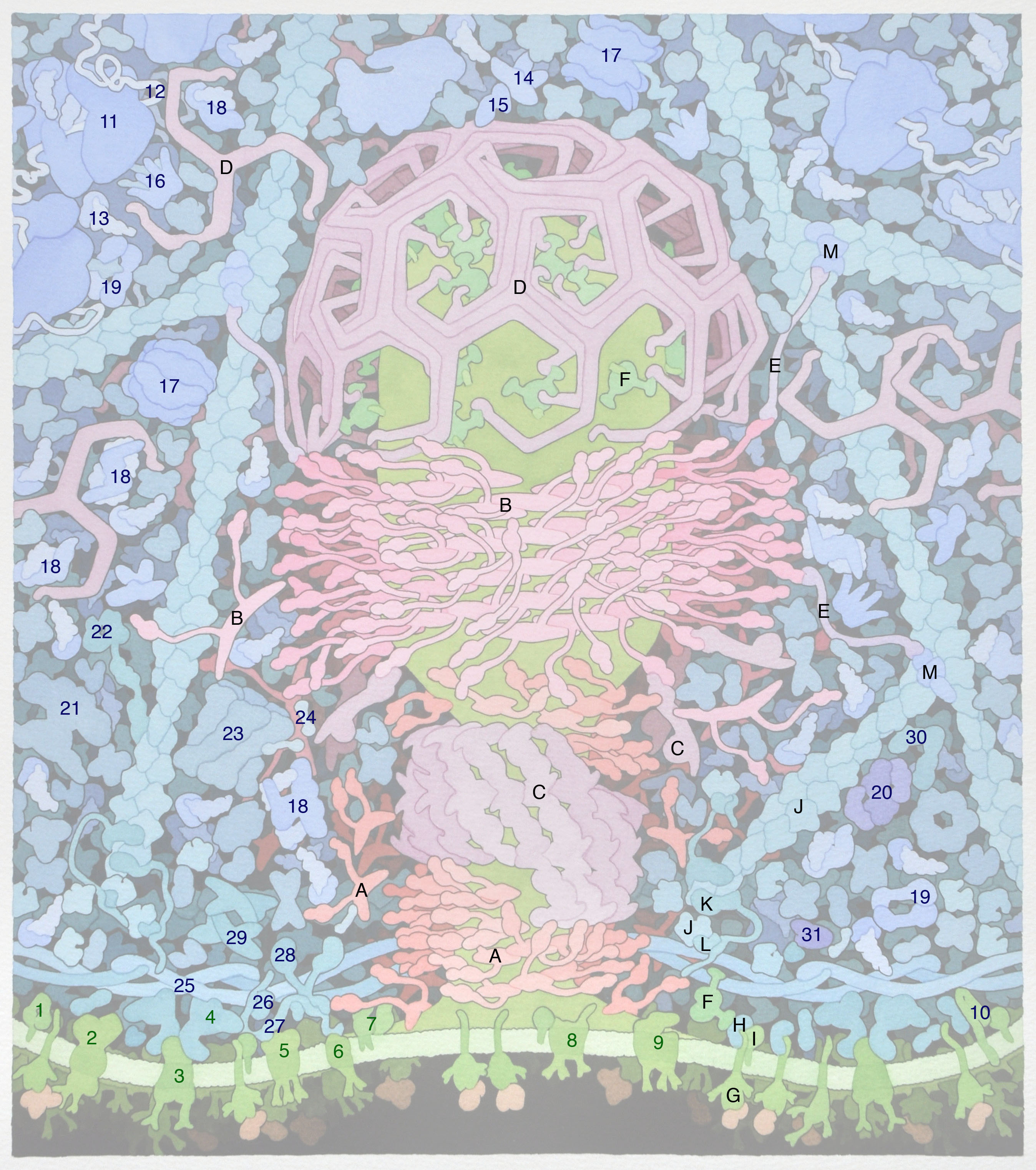
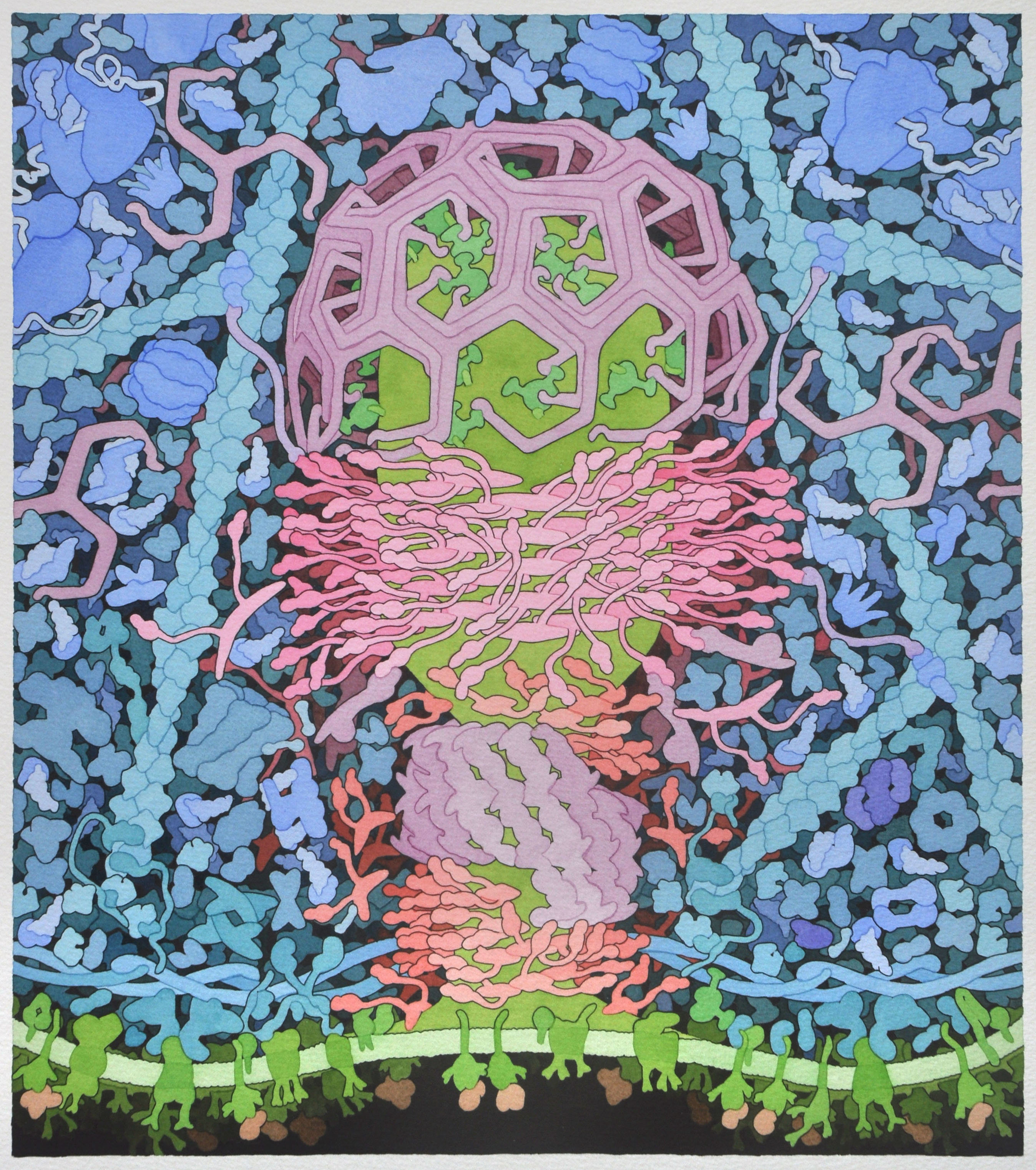
Here we explore one of Dr. Goodsell's molecular landscapes, Coated Pit (2012), in detail. As you work through the exercise, you will begin to 'see' the detail and make sense of all the colors and shapes. As you explore other landscapes by Dr. Goodsell, you may discover the progression of our knowledge from his earlier to more recent work. In the same way, you may discover that we now know more detail about some of the proteins than we did when the Coated Pit landscape was created. Dr. Goodsell's molecular landscapes thus also provide a snapshot of what was known when the landscape was created.

Based on 1uru .pdb and Uniprot P49418.
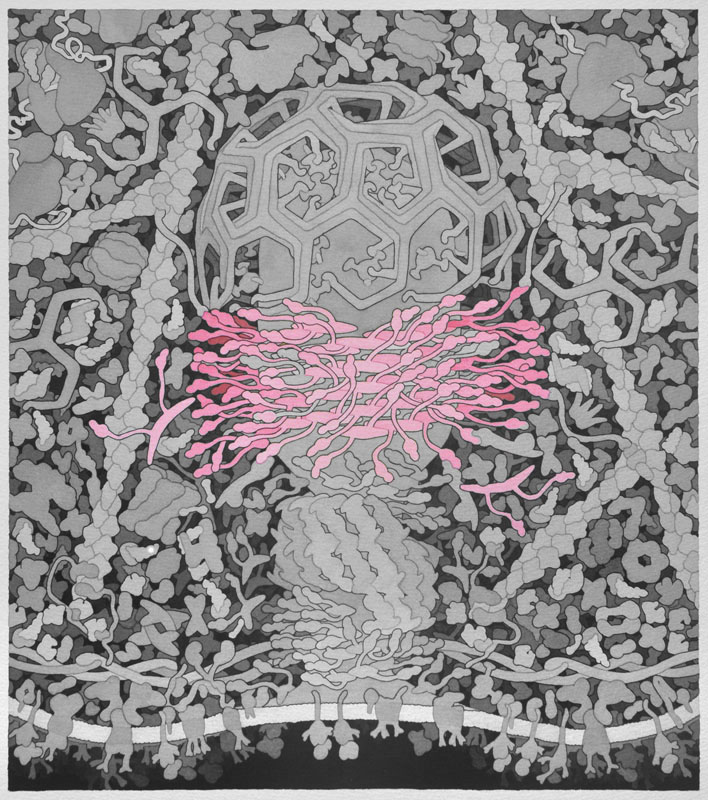
Bin-amphiphysin-rvs (BAR) - Proteins with BAR domains that sense and induce membrane curvature. The BAR family of proteins are very large, consisting of F-BAR proteins, I-BAR proteins, and N-BAR proteins. BAR proteins can also recruit dynamin to sites of clathrin coated pits and therefore promote endocytosis, as shown here. This is a homodimeric protein with monomers shown in separate colors.
Backbone PDB ID: 1uruThe F-BAR domain (FNBP1) is based on 2efl.pdb and Uniprot Q96RU3.
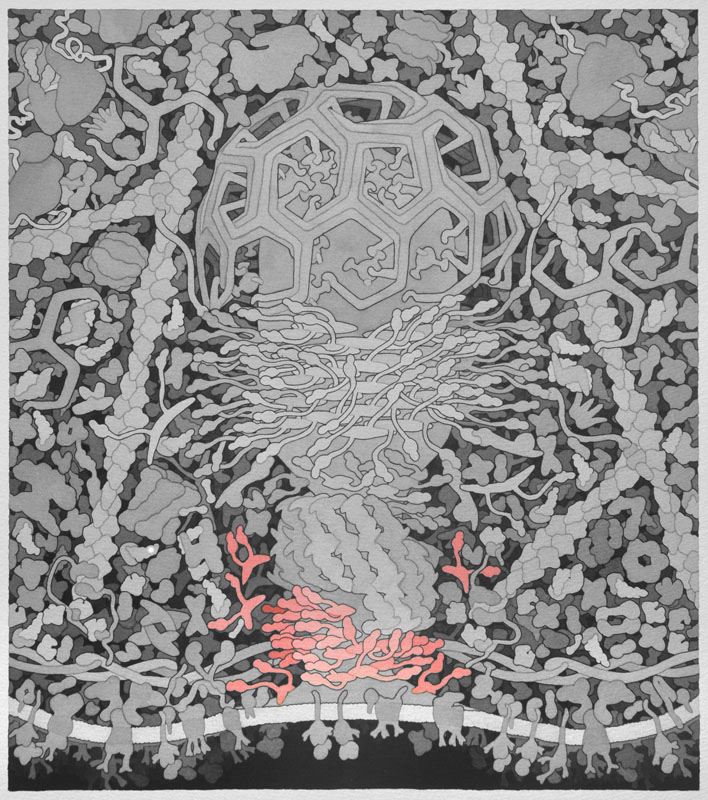
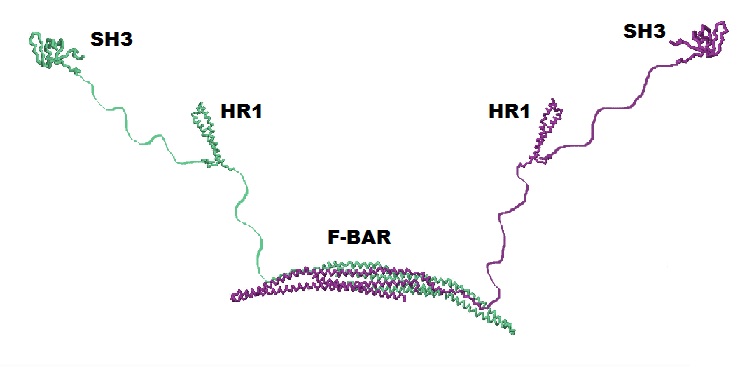
Cdc42 Interacting Protein 4 (CIP4) - Determines the curvature and shape of the formed vesicle during endocytosis via its F-BAR domain, a domain that can bind and tubulate lipid membranes. CIP4 also has an HR1 domain that interacts with active Cdc42 and an SH3 domain that interacts with actin associated proteins, which are also important in endocytosis. The Jmol image is only of the F-BAR domain of CIP4. This is a homodimeric protein with monomers shown in separate colors. Please refer to the picture below for a complete CIP4 protein containing all of its domains.
Based on EM structure and 2w6d.pdb.
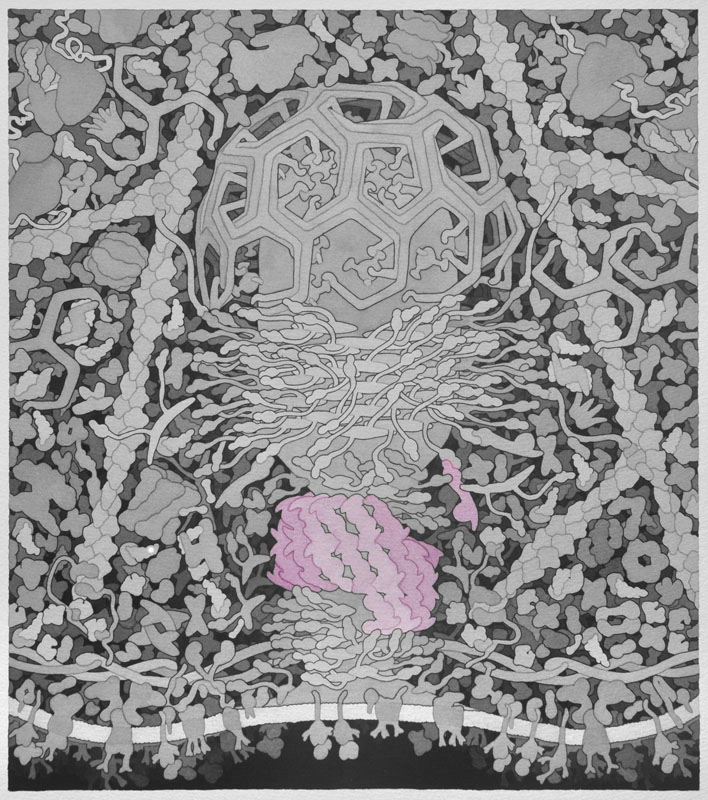
Dynamin - In the final steps of endocytosis, dynamin forms a spiral between the vesicle and the cellular membrane. Through GTP hydrolysis dynamin extends lengthwise and constricts eventually causing release of the vesicle into the cell. It also assists in division of organelles, cytokinesis, and microbial pathogen resistance. This is a homodimeric protein with monomers shown in separate colors.
Backbone PDB ID: 2w6dBased on 1xi4.pdb and Molecule of the Month on Clathrin.
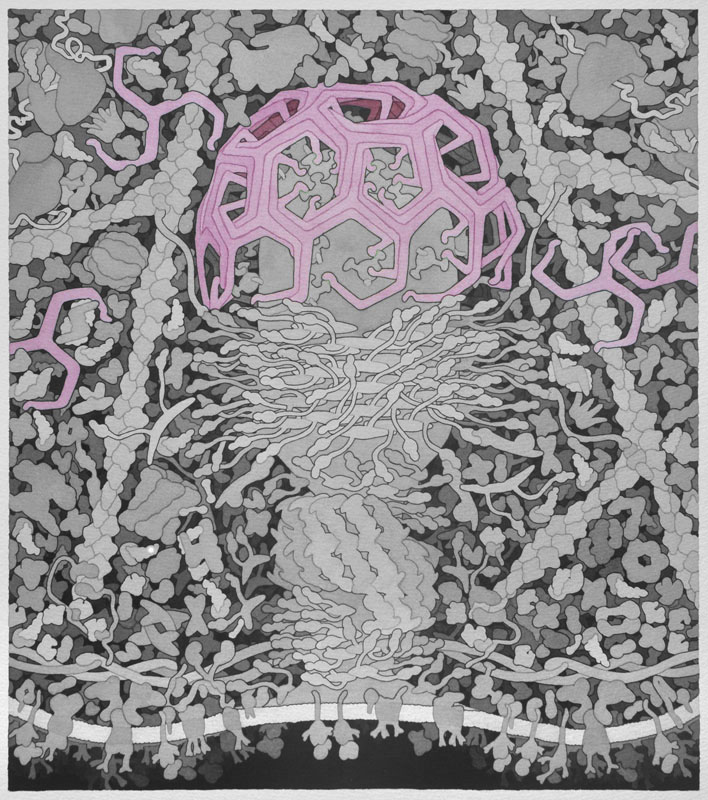
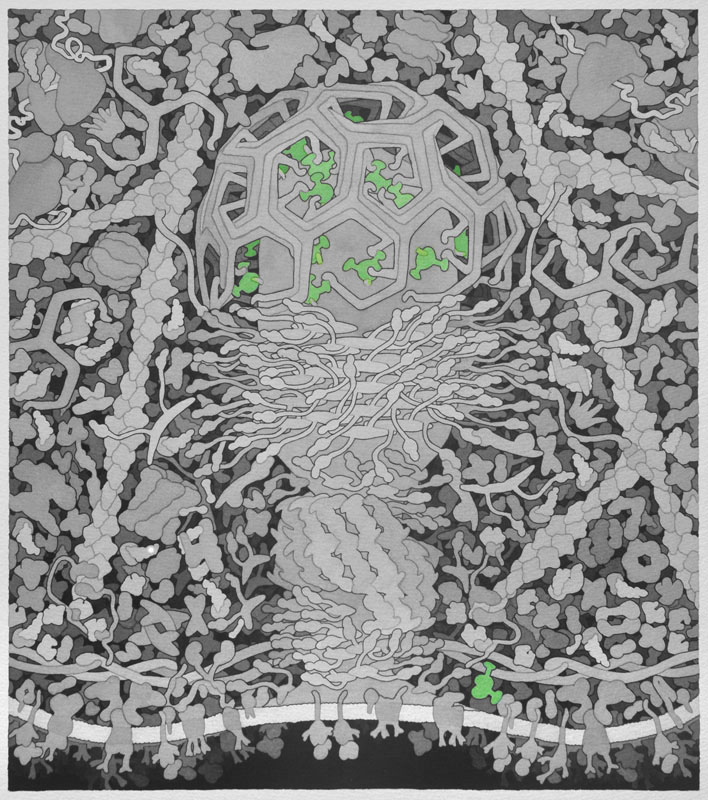
Clathrin - When receptors in the cell membrane bind cargo such as nutrients and other substances essential to the cell in the extracellular environment, adaptor proteins bind to the intracellular part of the receptor and recruit and promote the polymerization of clathrin triskelions at the membrane to start the invagination of the cell membrane to uptake the cargo during endocytosis. Clathrin also plays an important role in forming vesicles that bud from the Golgi apparatus. Once the vesicle is budded into the cytoplasm, clathrin rapidly disassembles. Above, only three triskelions are shown in different colors.
Backbone PDB ID: 1xi4Due to missing information in crystal structure, clathrin image in wireframe is not meaningful.
Based Uniprot P42768.
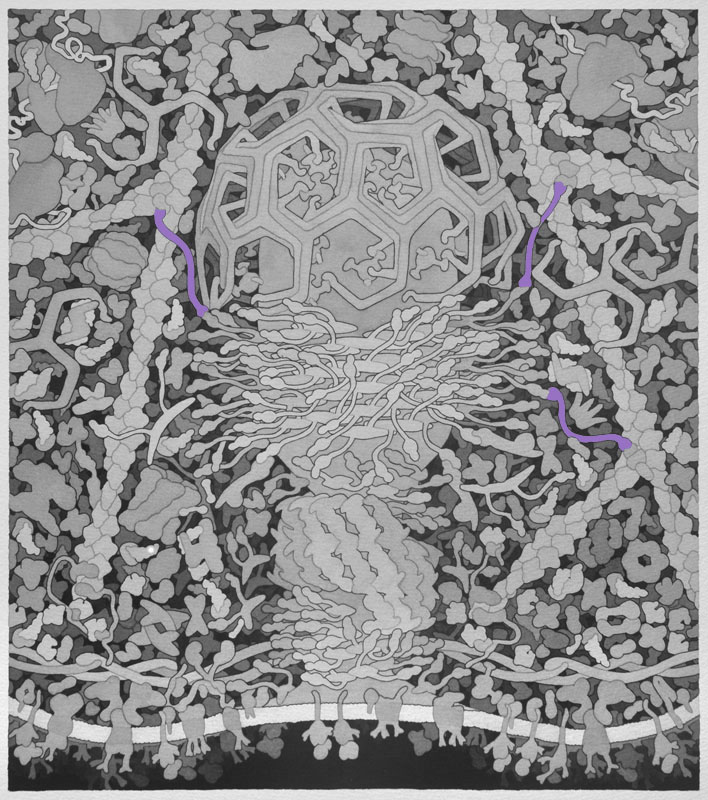
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP) - Activated by Cdc42 and PIP2. Involved in transduction of signals from receptors on the cell surface to the actin cytoskeleton. WASP binds to and activates the Arp2/3 complex, which causes actin filament branching.
No PDB file of entire structure available.
Based on 1gw5.pdb, 1ky7.pdb, 2g30.pdb and Molecule of the Month on Clathrin.
Adaptor - Recruited to cargo receptors in the cell membrane when nutrients and other substances essential to the cell need to be endocytosed. Adaptor proteins then recruit clathrin to deform the membrane and shape the vesicle.
Backbone PDB ID: 1vglBased on protein ERGIC-53, 3a4u.pdb, chain A.
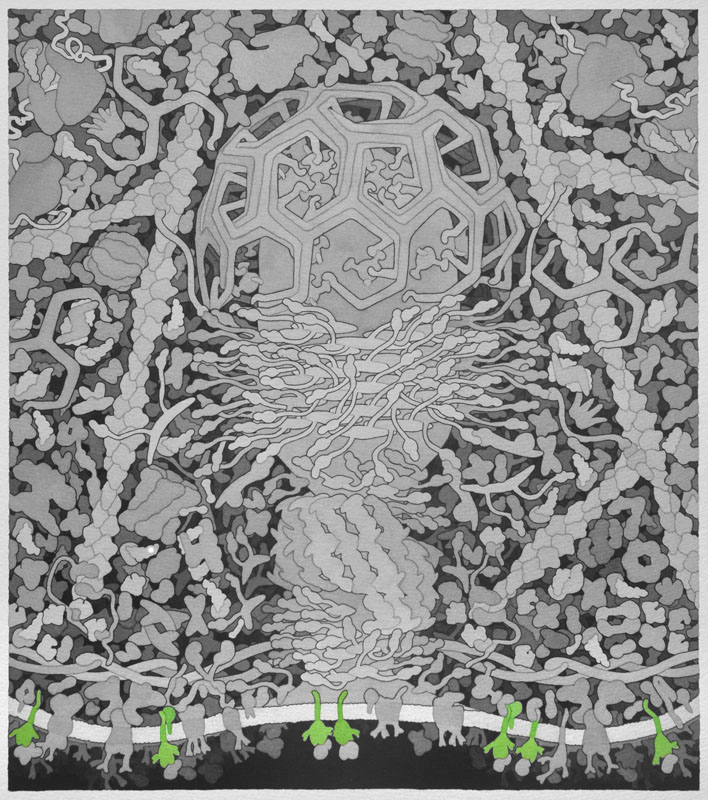
Cargo Receptor - Endocytosis is initiated when cargo such as nutrients and other substances essential to a cell attach to the extracellular binding sites of cargo receptors. Intracellular signals then recruit adaptor proteins.
Backbone PDB ID: 3a4uBased on 1j2j.pdb (domain of GGA bound to ARF1).
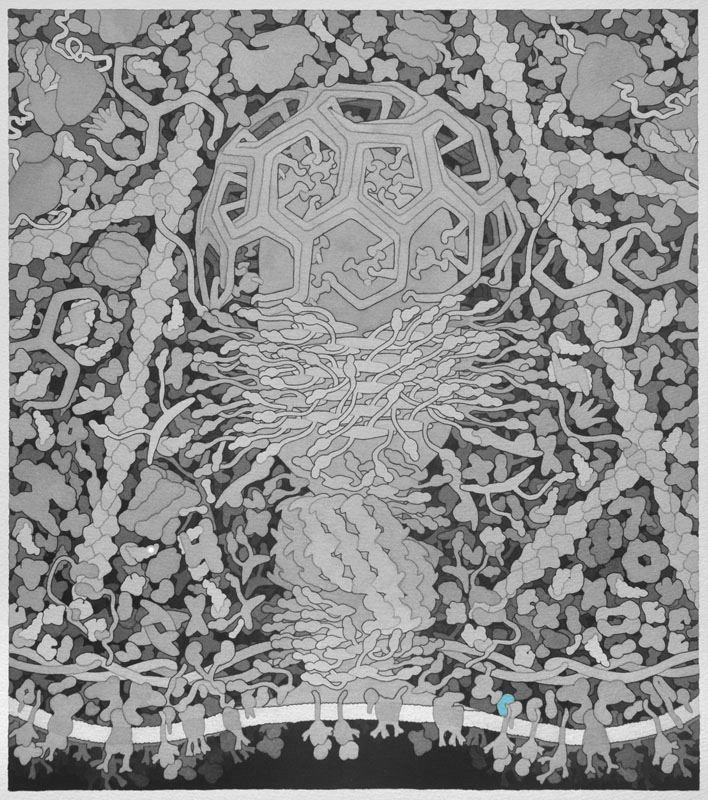
GGA - Vesicle coat proteins that regulate membrane trafficking mostly between the Golgi apparatus and lysosomes by interacting directly with adenosine diphosphate ribosylation factors, cargo, and clathrin.
Backbone PDB ID: 1j2jBased on 1rrf .pdb.
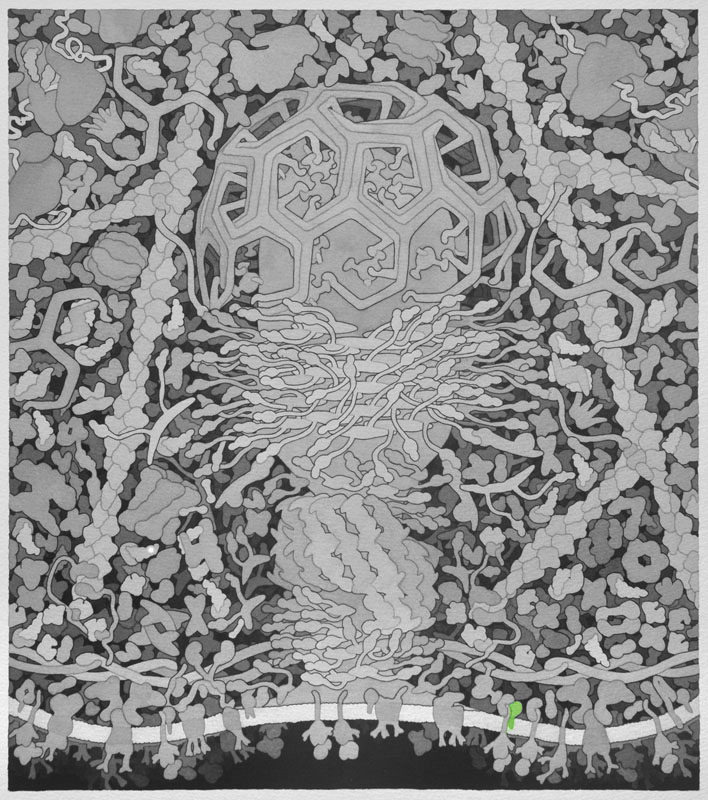
Adenosine Diphosphate Ribosylation Factor (ARF) - Generally associates with membranes and function as regulators of vesicular traffic and actin remodeling.
Backbone PDB ID: 1rrfMonomer based on 1atn.pdb, chain A. Short filament based on 1mvw.pdb(chains 1-9 and V-Z or 2y83.pdb.
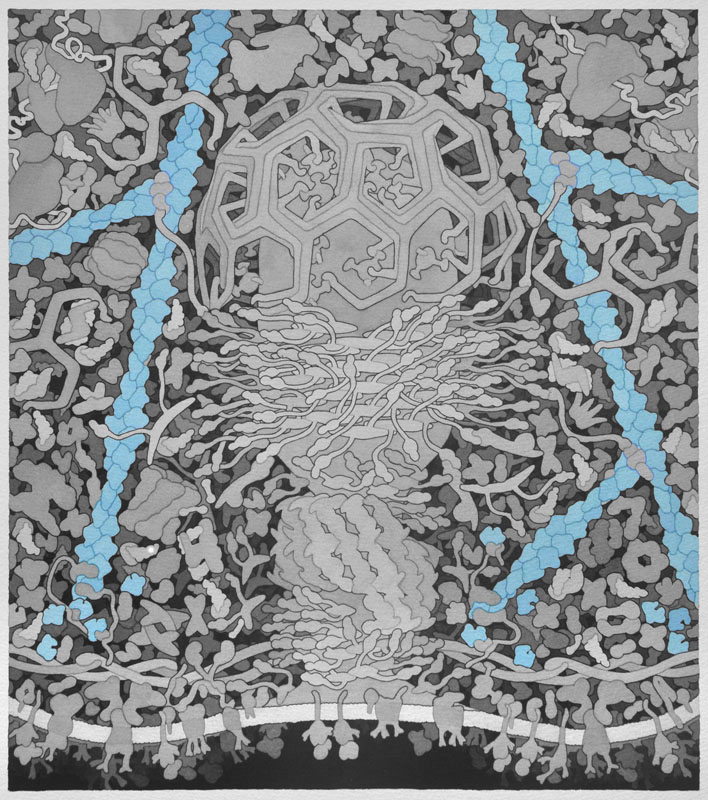
Actin -Actin monomers polymerize to form actin filaments that are one of the major components of a cells cytoskeleton. Actin is the primary polymer in cells that provides force for membrane movement. In endocytosis, the growing ends of actin filaments are directed towards the cell membrane, allowing the vesicle to detach and propel away from the membrane. Separate monomers are presented in different colors.
Backbone PDB ID: 2y83Based on 1y64.pdb (fragment of formin plus actin).
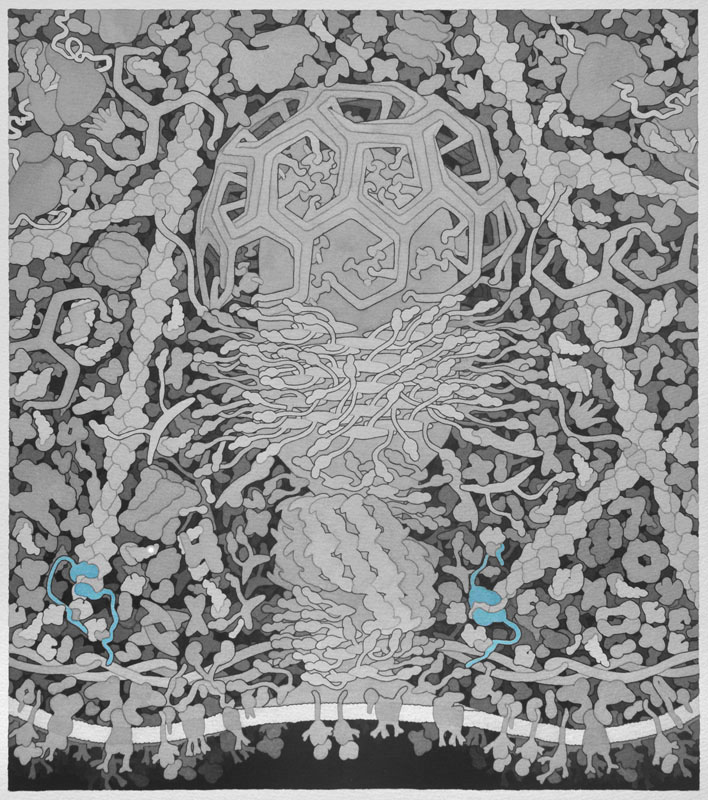
Formin - Proteins involved in the polymerization of actin that associate with the fast growing or barbed end of actin filaments. The above image shows the formin protein in green binding to an actin monomer in blue.
Backbone PDB ID: 1y64Based on 3chw.pdb (profilin plus actin plus formin-like peptide).
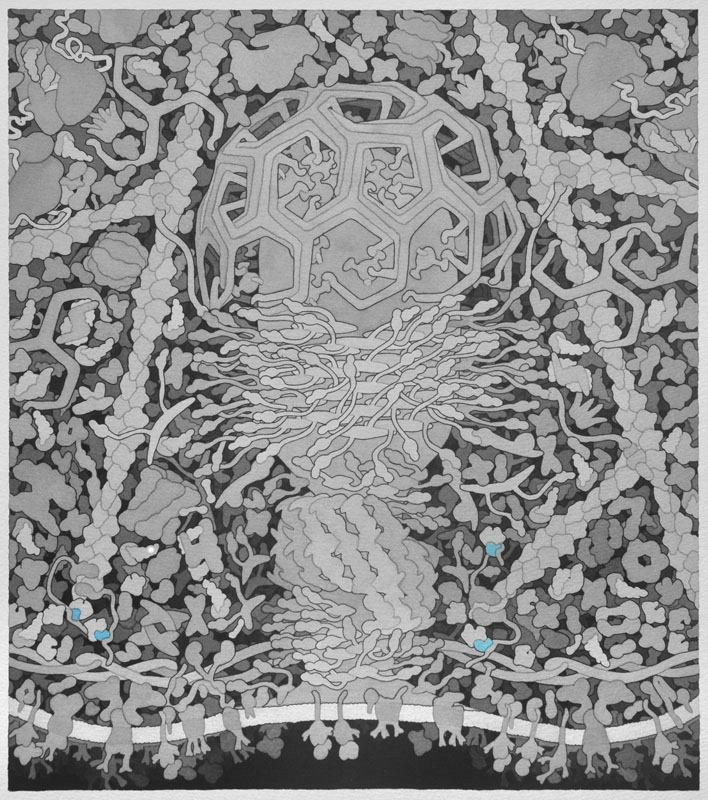
Profilin - Binds actin monomers, making them competent to polymerize into actin filaments. Profilin is in green, actin is in blue, and the olive-colored chain is a small peptide from a formin-like protein.
Backbone PDB ID: 3chwBased on 1k8k.pdb.
Actin Related Protein (Arp) 2/3 Complex - When activated by Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) or WASP-family verprolin-homologous protein (WAVE), the Arp 2/3 complex binds along existing actin filaments to create a nucleation point in which a new actin filament can grow, forming a branched actin network.
Backbone PDB ID: 1k8kThe following image labels additional proteins (1-31) that are present in the Coated Pit landscape.
